Predictability Chart Report
Detailed description of the Predictability Chart report in Jira Metrics Plugin, its construction and interpretation.
Overview
The Predictability Chart is a metric proposed by Kanban University to measure the stability and predictability of a team's workflow. This report helps assess how reliably a team can forecast task completion times.
Building the Predictability Chart
1. Data Collection
- Collect lead time or cycle time data for each task over a specific period.
- It's important to ensure data accuracy and cover a sufficient time range for statistical significance.
2. Percentile Calculation
- 50th percentile (median): The time value below which 50% of tasks are completed.
- 98th percentile: The time value below which 98% of tasks are completed.
3. Calculating the 98% / 50% Ratio
- Ratio = 98th percentile / 50th percentile
- This ratio shows the degree of variability in the process. A lower value means a more predictable process.
4. Plotting the Graph
- X-axis: Timeline (days, weeks, or months)
- Y-axis: Calculated 98% / 50% ratio for each period
- Points on the graph are connected with a line to visualize trends
Chart Structure
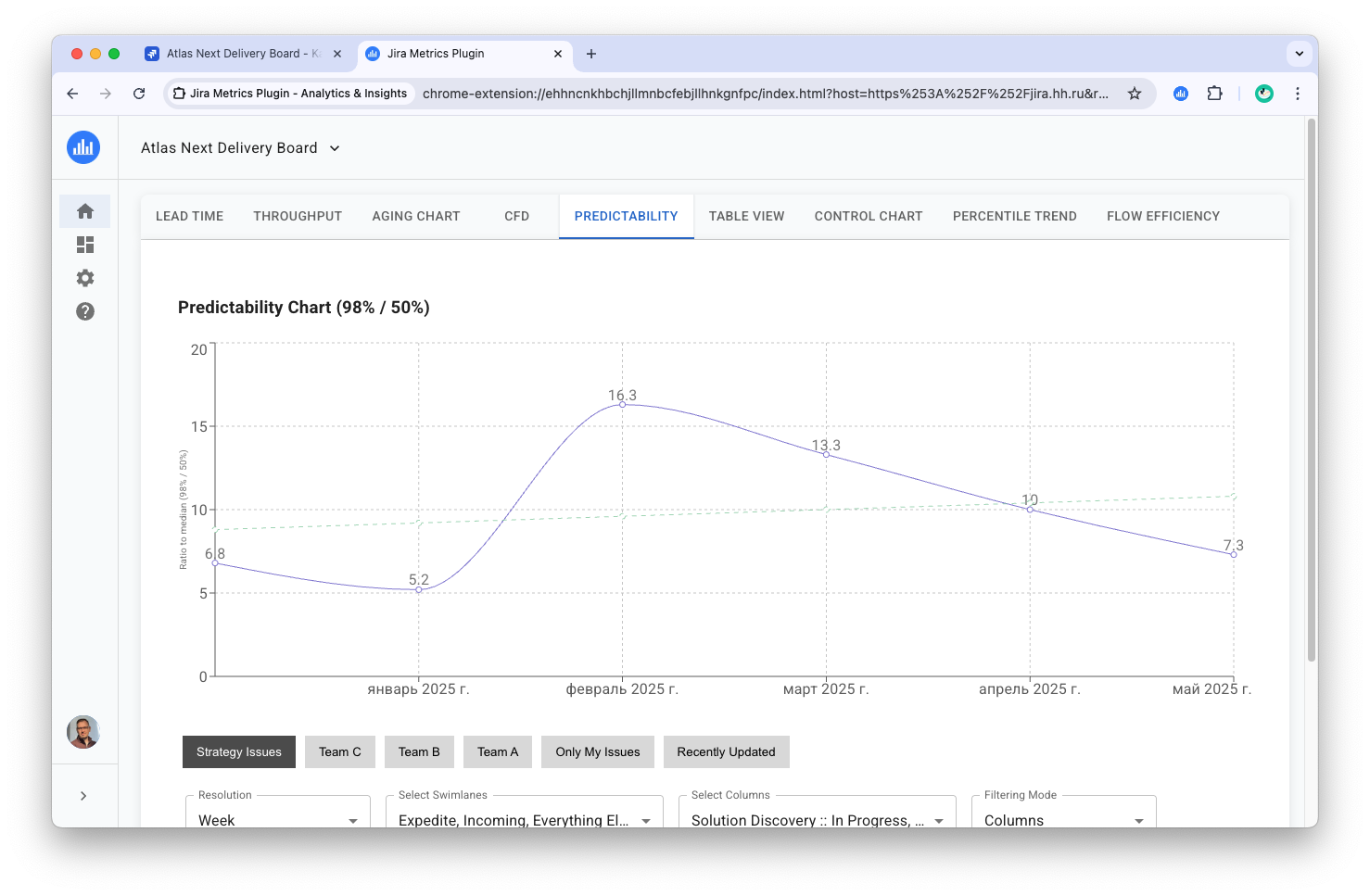
The chart shows a line representing the change in the 98% / 50% ratio over time. The values on the graph reflect the degree of process predictability.
Interpreting Values
- Value close to 1: Indicates high predictability and low process variability.
- Values from 1 to 2: Considered very good indicators.
- Values from 2 to 3: Indicate moderate predictability.
- Values above 3: Signal low predictability and high process variability.
Trend Analysis
- Decreasing ratio over time: Indicates process improvement and increased stability.
- Increasing ratio: May signal possible problems or changes in the process that require attention.
- Stable line: Indicates an unchanged, but not improving process.
Report Configuration
Below the chart are control elements:
- Resolution: Choose the time interval (day, week, month).
- Select Swimlanes: Filter by specific swimlanes.
- Select Columns: Choose columns for analysis.
- Filtering Mode: Select filtering mode (Activity/Completion).
- Completion Columns: Choose completion columns (for Completion mode).
Practical Usage Tips
-
Regular monitoring: Update and analyze the chart regularly to detect deviations in a timely manner.
-
Finding causes of variability: For high ratios, analyze tasks with long completion times to identify causes of delays.
-
Implementing improvements: Use the data obtained to optimize processes, eliminate bottlenecks, and increase efficiency.
-
Comprehensive analysis: Consider the Predictability Chart in combination with other metrics, such as Lead Time and Throughput, for a full analysis.
-
Context consideration: Take into account the specifics of the project and team when interpreting values.
Metric Limitations
- Does not account for task size or complexity.
- May be sensitive to outliers, especially with a small number of tasks.
- Does not reflect the reasons for changes in predictability.
Conclusion
The Predictability Chart is a valuable tool for assessing the stability and predictability of the development process. Regular analysis of this metric will help you identify areas for improvement, optimize work processes, and increase team efficiency.